Java is a popular programming language for the system software development and web application. You need to install Java Development Kit (JDK) and Java Runtime Environment (JRE) for the setup of the Java development environment. JDK compiled the source java file and make a java class file. JRE is used to run that intermediate class file. This tutorial will guide you to install Oracle Java 11 LTS version on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS Xenial system.
Step 1 – Prerequsities
Before beginning the installation login to shell as the sudo user and install some required packages.
sudo -i apt install wget libasound2 libasound2-data
Step 2 – Download Java 11
Download the latest Java SE Development Kit 11 LTS debian file release from its official download page or use following commands to download from command line.
wget --no-cookies --no-check-certificate --header "Cookie: oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/11+28/55eed80b163941c8885ad9298e6d786a/jdk-11_linux-x64_bin.deb
Step 3 – Install Java 11 on Ubuntu 16.04
Use default Debian package installer (dpkg) to install downloaded Java on your system. Simply execute the following command on terminal
dpkg -i jdk-11_linux-x64_bin.deb
Then configure Java 11 as the default version on your system.
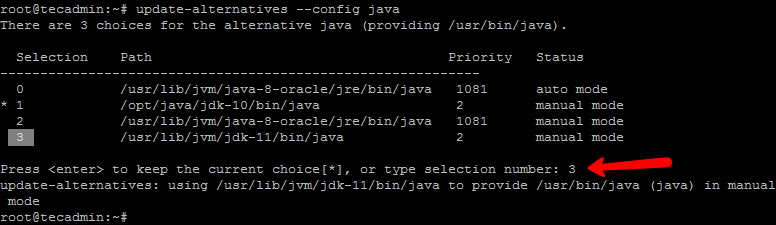
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-11/bin/java 2 update-alternatives --config java
According to the above screenshot, there are 3 versions installed. Java 11 is listed on number 3, So entered 3 and press Enter. Now Java 11 is installed as default Java version on my Ubuntu 16.04 system.
There are some other binaries to set as default for JDK installation. Execute the commands to set javac and jar as default:
update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/jar jar /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-11/bin/jar 2 update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/javac javac /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-11/bin/javac 2 update-alternatives --set jar /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-11/bin/jar update-alternatives --set javac /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-11/bin/javac
Step 4 – Verify Java Version
Now check the installed Java version on your system using the following command.
java -version java version "11" 2018-09-25 Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment 18.9 (build 11+28) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM 18.9 (build 11+28, mixed mode)
Step 5 – Setup Java Environment Variables
Most of the Java-based applications uses environment variables to work. Create an script as below. Now set all the required environment variables for Java. This file will automatically reload settings on system reboot.
sudo nano /etc/profile.d/jdk.sh
Add/Update following values:
export J2SDKDIR=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11 export J2REDIR=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11 export PATH=$PATH:/usr/lib/jvm/java-11/bin:/usr/lib/jvm/java-11/db/bin export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11 export DERBY_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11/db
Save you file and exit. Now load these setting to current active shell also
source /etc/profile.d/jdk.sh
You have successfully installed Java 11 on Ubuntu system.